A Characteristic Feature of Any Form of Chromatography Is
Use of molecules that are soluble in water. The term chromatography is derived from Greek chroma meaning colour and graphein meaning to write.

Chromatography An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Use of an Inert Study Resources.

. Size-exclusion chromatography SEC is also known as gel permeation chromatography GPC or gel filtration chromatography and separates molecules according to their size or more accurately according to their hydrodynamic diameter or hydrodynamic volume. This phase is always composed of liquid or a gaseous component Separated molecules. Characteristic feature of any form of chromatography is the ___ A.
Characteristic feature of any form of chromatography is the __ 15 1 Point Use of molecules that are soluble in water. Calculation of an Rf value for the molecules separated. Smaller molecules are able to enter the pores of the media and therefore molecules are trapped and removed from the.
Use of a mobile and a stationary phase. Use of a mobile and a stationary phase. Solute equilibrates between the mobile phase and the stationary liquid.
Calculation of an Rf value for the molecules separated. Calculation of an Rf value for the molecules separated. O Use of an inert carrier gas.
N A characteristic feature of any form of chromatographyI is the Hintl use of molecules that are soluble in water. Use of molecules that are soluble in water. In this process we apply the mixture to be separated on a stationary phase solid or liquid and a pure solvent such as water or any gas is allowed to move slowly over the.
Inverse gas chromatography IGC is a versatile powerful sensitive and relatively fast technique for characterizing the physicochemical properties of materials. Chromatography technique for separating the components or solutes of a mixture on the basis of the relative amounts of each solute distributed between a moving fluid stream called the mobile phase and a contiguous stationary phase. The separation is based on differential partitioning between the mobile and stationary phases.
Subtle differences in a compounds partition coefficent result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. A commonly used tool to observe separation of biomolecules in biochemistry identifying illicit drugs or dyes in fibers in forensic chemistry analyzing components of medicinal plants etc. Based on components of a mixture being differentiated by exposure by two competing phases.
Compounds in the sample interact different with both phases and are therefore held back stronger or lesser. N Calculation of an Rf value for the molecules separated. This results in the accumulation of compounds that interact similar at some point in the system with some chromatographys.
A characteristic feature of any form of chromatography is the. Chromatography is the technique for the separation purification and testing of compounds. Use of an inert carrier gas.
A characteristic feature of any form of chromatography is the. Based on this approach three components form the basis of the chromatography technique. The mobile phase may be either a liquid or a gas while the stationary phase is either a solid or a liquid.
Calculation of an Rf value for the molecules. Use of molecules that are soluble in water. Paper Chromatography Column Chromatography Thin Layer Chromatography Gas Chromatography Size Exclusion Chromatography Ion Exchange Chromatography Q1.
Thus characteristic feature of any form of chromatography is use of mobile and a stationary phase and seperate them on the basis of. There is always a mobile e. Use of an inert carrier gas.
Use of a mobile and a stationary phase. In addition to this chromatography is also an important process for the separation of substances of the mixture. A long retention time in gas chromatography is indicative of a substance with a strong adsorption on to the stationary phase.
In Column chromatography the stationary phase is made of_ and the mobile phase is made of 1 Point 0. In Chromatography the retardation factor R f are used for identification of components. Use of molecules that are soluble in water.
Gel - GC solid - LCs GPC. Chromatography refers to a physical method of separation in which the analytes are separated based on their distribution between two phases a stationary phase and a mobile phase. Use of a mobile and a stationary phase.
A characteristic feature of any form of chromatography is the A. A characteristic feature of any form of chromatography is the a. A high Rf value is indicative of a substance that adsorbs strongly onto the stationary phase.
GPC and a stationary phase liquid. The result is that the components are resolved into consecutive rectangular zones of highly concentrated pure substances rather than solvent. Ion Exchange Chromatography.
Due to its applicability in determining surface properties of solids in any form such as films fibres and powders of both crystalline and amorphous structures IGC became a popular technique for surface. This form of chromatography is based on a thin film formed on the surface of a solid support by a liquid stationary phase. Calculation of an Rf value for the molecules separated.
Subtle differences in a compounds partition coefficent result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Displacement chromatography is a chromatography technique in which a sample is placed onto the head of the column and is then displaced by a solute that is more strongly sorbed than the components of the original mixture. A high R f and a low R t retention time.
This phase is always composed of a solid phase or a layer of a liquid adsorbed on the surface a solid support. Use of an inert carrier gas. Use of an inert carrier gas.
Gas - GC Liquid - HPLC. Hence a characteristic feature of any form of chromatography is the use of a mobile and a stationary phase. In gas chromatography the mobile phase is an inert gas and the stationary phase is a nonvolatile liquid gasliquid chromatography.
View Test Prep - chromatography from CHEMISTRY 101 at Yale Hs. The characteristic feature of any form of chromatography is the absorption of a stationary phase in another medium. Thus characteristic feature of any form of chromatography is use of mobile and a stationary phase and seperate them on the basis of their retardation factor ie Rf value.

Difference Between Solid Liquid And Gas In Tabular Form States Of Matter Simplified Solid Liquid Gas States Of Matter Intermolecular Force
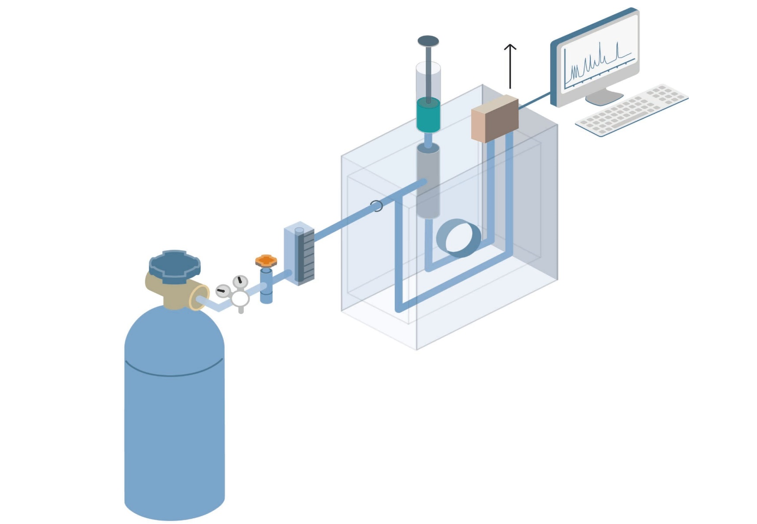
Introduction To Gas Chromatography Principles Characteristics And Process Creative Proteomics Blog

Paper Chromatography Definition Method Uses Britannica

Pure Substances And Mixtures Bundle Physical And Chemical Properties Scaffolded Notes Chemistry Activities

Characteristics Of Dna Polymerase I From An Extreme Thermophile Thermus Scotoductus Strain K1 Saghatelyan 2021 Microbiologyopen Wiley Online Library

Basic Overview On Gas Chromatography Columns Rahman Major Reference Works Wiley Online Library

Chromatography Definition Types Facts Britannica

Chromatography An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Exhaled Breath Analysis Breath Analysis Offers A Window On Lung Physiology And Disease And Is Rapidly Evolving As A Ne Respiratory System Analysis Physiology

Understanding The Role And Sync Of Gc Capillary Column And Its Detector Column Gas Chromatography Detector

Different Types Of Mass Spec Instruments Mass Spectrometry Nursing Student Tips Infographic

Non Contact Pyrometers Characteristics Characteristics Radiation Surface

Chromatography An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Chromatography An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Principles Of Chromatography Stationary Phase Article Khan Academy

Chromatography Definition Types Facts Britannica

Chromatography An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

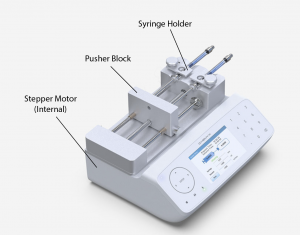
Comments
Post a Comment